![]()

May 10, 2023
IPv4 and IPv6 Load Balancing, The Best Network Management!
As we move deeper into the digital age, the internet has become a quintessential part of our daily life. This has led to an exponential increase in the number of people using the Internet, which, in turn, has put an immense load on the internet’s infrastructure. One of the critical tools used to handle this increased load is IPv4 and IPv6 load balancing, which is the process of distributing the workload across multiple servers to ensure that no one server is overburdened.
What is IPv4 and IPv6 Load Balancing?
With IPv4 and IPv6 both enabled, load balancing became a key component in effectively managing network traffic and ensuring optimal performance for applications and other critical services. At its core, IP load balancing involves distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers, typically in a data centre environment. This process helps to distribute workloads evenly across server resources, improving response times and reducing the risk of bottlenecks or service interruptions.
There are many different approaches to IP load balancing, ranging from hardware-based solutions to software-based alternatives. Generally speaking, the most effective IP load balancing solutions utilize a combination of both hardware and software components, leveraging the strengths of each to create a highly reliable, high-performance network environment.
Regardless of the specific approach chosen, IP load balancing is a critical component of modern network design, providing organizations with the ability to ensure high levels of performance, reliability, and availability for critical applications and services. By leveraging the power of load balancing, organizations can improve the overall user experience, reduce the risk of service downtime and ensure maximum uptime for essential business operations.
Differences Between IPv4 and IPv6
Internet Protocol (IP) is the communication protocol that enables devices to connect and communicate over the Internet. IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) was the standard protocol for over three decades until IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) was introduced.
One of the significant differences between IPv4 and IPv6 is the number of unique addresses available. IPv4 uses a 32-bit address, which allows approximately 4 billion unique addresses. With the increasing use of the internet and the rise of connected devices, the availability of IPv4 addresses has become scarce. In contrast, IPv6 uses a 128-bit address, enabling approximately 3.4 x 10^38 unique addresses, which makes it an ideal choice for future developments in the Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communication. IPv6 also offers additional features compared to IPv4, such as improved security through IPSec, efficient multicasting, and simplified network configurability through auto-configuration.
IPv4 and IPv6 Load Balancing Techniques
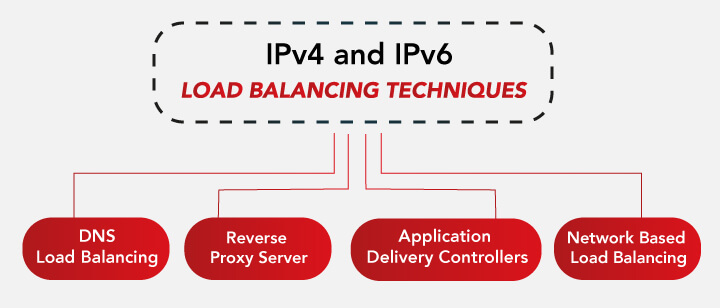
DNS Load Balancing
One of the most common techniques for IPv4 and IPv6 load balancing is round-robin DNS (Domain Name System) load balancing. In this method, multiple IP addresses of servers or paths are assigned to a single domain name, and the DNS server randomly assigns the IP address to the requesting client. Round-robin DNS load balancing distributes traffic evenly among the available servers or paths, thus achieving high availability and reliability. However, it does not consider the server’s current load or performance, and therefore, it may not be suitable for all scenarios.
Reverse Proxy Server
Another technique for IPv4 and IPv6 load balancing is the use of reverse proxy servers. This technique involves placing a reverse proxy server between the client and the servers or paths. When a client requests a resource, the reverse proxy server forwards the request to one of the servers or paths based on specific algorithms, such as the least-connection method, the fastest-response time method, or the IP-hash method. Reverse proxy servers provide several benefits such as load balancing, SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) offloading, and content caching. However, they also introduce latency and single-point-of-failure risks.
Application Delivery Controllers
Application delivery controllers (ADC) are a popular option for IPv4 and IPv6 load balancing. An ADC is a specialized device that provides advanced traffic management, optimization, and security features. It distributes traffic based on various algorithms such as round-robin, least-connection, IP-hash, and SSL session ID. ADCs also provide advanced features such as content caching, application acceleration, and SSL offloading. However, they are expensive and require specific skills to configure and maintain.
Network-Based Load Balancing
Network-based load balancing can be achieved using multilayer switches or routers. In this technique, the switch or router distributes traffic based on Layer 2 to Layer 5 packet information, such as source and destination IP addresses, protocol types, and port numbers. Multilayer switches or routers provide high-speed and efficient load balancing without introducing latency or a single point of failure. However, they may not be suitable for all scenarios, such as complex applications or dynamic network environments.
Benefits of IPv4 and IPv6 Load Balancing
Load balancing can improve network performance and reliability in IPv4 and IPv6 environments in the following ways:
- Increased Capacity: Load balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers, increasing the capacity of the network and reducing the chances of bottlenecks or overloading.
- Redundancy: Load balancing provides redundancy by redirecting traffic to alternate servers if a primary server fails or becomes unavailable. This ensures that the network remains available even if one or more servers fail.
- Reduced Downtime: By spreading incoming traffic across multiple servers, load balancing can help reduce downtime and ensure that the network remains available even during peak usage periods.
- Better Resource Utilization: Load balancing helps to balance the resources (CPU, memory, etc.) across multiple servers. This ensures that resources are being utilized optimally, without any server running idle.
- Fast Response: Load balancing distributes network traffic across multiple servers, ensuring that each server has fewer requests to handle. This helps to improve the response time of the network, providing a better user experience.
- IPv6 Compatibility: Load balancing is compatible with both IPv4 and IPv6 environments, which helps to ensure that the network can handle the increasing number of IPv6 requests as more devices transition to this protocol.
In conclusion, load balancing is a critical aspect of IPv4 and IPv6 networks to achieve high availability, reliability, and performance.
Recent Posts
Archives
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- October 2018
- September 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- November 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- August 2015
Completely synergize resource is taxing relationships via premier are man niche markets. Professionally cultivate one to one customer.
Recent News
Blockchain Technology: Revolutionizing IP Management
October 30, 2024
Understanding IPv4Mall’s Trusted Partnerships
October 26, 2024
IP Warming: Taming the Wild West of Email Delivery
October 24, 2024
Tags
Archives
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- October 2018
- September 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- November 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- August 2015
North America :
Phone: +1-310-299-0944
Headquarters: 18C-3107 av. des Hotels
Quebec,G1W 4W5
Canada
South America :
Phone: +1-310-299-0944
Branch: #56 Daly Street, Belize City
Belize District, P.O. Box 1825
Belize









Recent Comments