![]()

July 16, 2023
Classless IP Addressing: The Efficient Approach to Network Design
In computer networking, an IP address is a unique identifier assigned to every device connected to the network. IP addresses are crucial for effective communication and identification of devices across the internet. In the early days of networking, IP addresses were defined in a set of classes. However, this class-based system was inefficient as it led to the waste of a large number of IP addresses. To address this concern, classless IP addressing was introduced. In this blog post, we will discuss more information about classless IP addressing with example.
What is Classless IP Addressing?
Classless IP Addressing, also known as Variable-Length Subnet Masking (VLSM), is a more flexible and efficient approach to assigning IP addresses to hosts within a network. It is a departure from the older, and now obsolete, Classful IP addressing which relied on rigid network classes to define the host range.
In classful addressing, an IP address was divided into three different classes, A, B, and C, depending on the number of network bits used to identify the network and host bits used to identify the hosts. These network classes restricted the number of available IP addresses for a given network, leading to a significant waste of IP addresses. For instance, this meant that a small company with only 10 hosts would still be allocated a Class C network with 254 available IP addresses, wasting valuable network resources.
Classless IP addressing, on the other hand, removes the restriction on the number of IP addresses available to a network by allowing the division of an IP address into multiple subnets, each with a variable-length subnet mask (VLSM). This allows for the allocation of smaller blocks of IP addresses, which conserves IP address space and is more flexible in network design.
In Classless IP addressing, a network administrator can match the subnet mask to the size of a network, for example, if there are only ten hosts, it is possible to use a subnet mask that provides a maximum of 14 host addresses, thus reducing waste in addressing. Additionally, it allows for multiple host ranges within a network, which can result in lower network traffic, faster data transmission, and better network security, as it becomes easier to segment a network into more secure subnets.
Classless IP addressing is essential at a time when the demand for IP addresses has exceeded the available pool, and the IPv4 protocol nears exhaustion. As the world moves towards the adoption of IPv6, which provides a significantly larger number of IP addresses, understanding the principles of Classless IP addressing becomes crucial in efficient network design.
Advantages of Classless Addressing
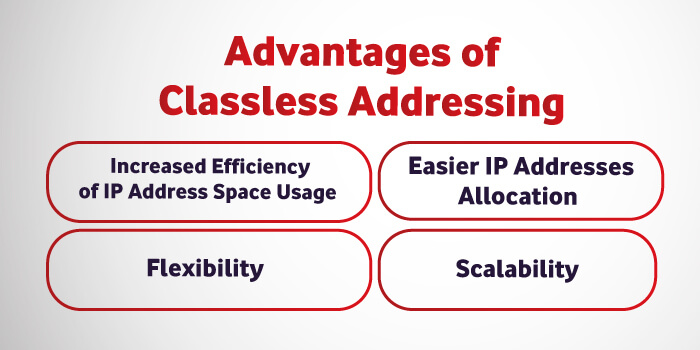
Increased Efficiency of IP Address Space Usage
One of the primary benefits of classless IP addressing is that it allows for more efficient use of IP address space. With classful addressing, an organisation would need to request addresses based on the largest potential network it would need to create. This often led to a significant waste of IP addresses, as many smaller networks would be assigned larger pools of addresses than they needed. This problem was particularly pronounced for organisations that needed to manage a large number of smaller networks. Classless addressing eliminates this issue by allowing networks of any size to use only the number of addresses it requires.
Flexibility
Another advantage of classless addressing is that it provides greater flexibility in network design. With classful addressing, the network address was predetermined by the class of the IP address being used. This often led to inefficiencies in network design, as networks had to be structured around the available address classes. With classless addressing, network designers have much greater freedom to structure their networks to fit their organisation’s specific needs and requirements.
Easier IP Addresses Allocation
Classless addressing also makes it easier to allocate IP addresses. Since IP addresses can be assigned more efficiently, organisations can request smaller blocks of addresses as needed rather than having to request an entire class. This reduces the administrative burden of managing IP address allocations and enables greater flexibility in network design.
Scalability
Finally, classless IP addressing is more scalable than classful addressing. As the number of networks on the internet has grown, it has become increasingly difficult to allocate IP addresses to connect the growing number of devices. Classless addressing allows for more efficient use of IP address space, which in turn enables more devices to be connected to the internet.
Classless Subnetting Examples
Several examples of classless subnetting illustrate the importance and benefits. For instance, if an organisation wants to create a private network within its premises, it can use classless subnetting to divide its IP address block into several smaller subnets that can be managed independently. This approach reduces the amount of broadcast traffic and improves network performance by limiting the number of devices that communicate with each other.
Another example of classless subnetting is in large organisations with multiple departments. Each department can be assigned a unique IP address block, which can be further subdivided into smaller subnets to accommodate different teams within each department. This approach makes it easier to isolate network issues and monitor traffic flow within each department without affecting other areas of the organisation.
In addition, classless subnetting can also be used to accommodate different types of devices on a network, such as printers, servers, and workstations. Each device can be assigned a unique IP address from a subnet that is specific to its function. For example, printers can be assigned to a separate subnet to prevent unnecessary traffic on the main network, which can improve overall network performance.
In conclusion, Classless IP Addressing or VLSM is a flexible and efficient approach to network design. It provides a wide range of IP addresses and reduces wastage of resources. It also allows for finer network segmentation, which improves security and enhances network speeds. Therefore, network administrators need to migrate from classful to classless IP addressing to ensure efficient use of network resources and streamline network operations.
Recent Posts
Archives
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- October 2018
- September 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- November 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- August 2015
Completely synergize resource is taxing relationships via premier are man niche markets. Professionally cultivate one to one customer.
Recent News
Blockchain Technology: Revolutionizing IP Management
October 30, 2024
Understanding IPv4Mall’s Trusted Partnerships
October 26, 2024
IP Warming: Taming the Wild West of Email Delivery
October 24, 2024
Tags
Archives
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- October 2018
- September 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- November 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- August 2015
North America :
Phone: +1-310-299-0944
Headquarters: 18C-3107 av. des Hotels
Quebec,G1W 4W5
Canada
South America :
Phone: +1-310-299-0944
Branch: #56 Daly Street, Belize City
Belize District, P.O. Box 1825
Belize









Recent Comments